
A Comprehensive Supply Chain for Core Intermediates in Diabetes Treatment
End-to-end supply chain for anti-diabetic intermediates. Covering DPP-4, SGLT-2 inhibitors & GPR40 agonists. Stable, compliant, scalable.
Table of Contents
As a synthetic chemist with 20 years of experience in API R&D, I’ve encountered countless molecular structures. However, orforglipron’s molecular structure stands out for its ingenious non-peptide design, defying the ironclad rule that GLP-1 agonists must be administered by injection.
Today, I’ll provide an in-depth analysis of the workings of this revolutionary drug from a medicinal chemist’s perspective.
Traditional GLP-1 drugs (such as semaglutide and liraglutide) are peptides and must be administered by injection for the following reasons:
– Gastric acid degradation: The highly acidic environment of the stomach breaks down peptide bonds
– Enzymatic degradation: Gastrointestinal proteases hydrolyze peptide chains into amino acids
– Excessive molecular weight: Peptide drugs typically have molecular weights >1000 Da, making them difficult to cross the intestinal barrier
Orforglipron’s breakthrough lies in its use of a completely non-peptide, small molecule structure (molecular weight of only 357.44 Da). Its design is fundamentally embodied in the following key aspects:
Feature Comparison | Traditional peptide GLP-1 agonists | Orforglipron |
Molecular type | Peptide (31-44 amino acids) | Non-peptide small molecules |
Molecular weight | ~4000Da | 357.44Da |
Dosage | Subcutaneous injection | oral |
Stability | Needs to be refrigerated, easily degraded | Stable at room temperature, not easily hydrolyzed by enzymes |
Absorption efficiency | Bioavailability ~80% | Bioavailability ~60-70% |
> ✅ From a synthetic chemistry perspective: By introducing an aryl pyrimidine backbone as the core structure and optimizing the lipophilicity of the side chains, we aim to make the molecule both resistant to gastrointestinal degradation and possess sufficient membrane permeability.
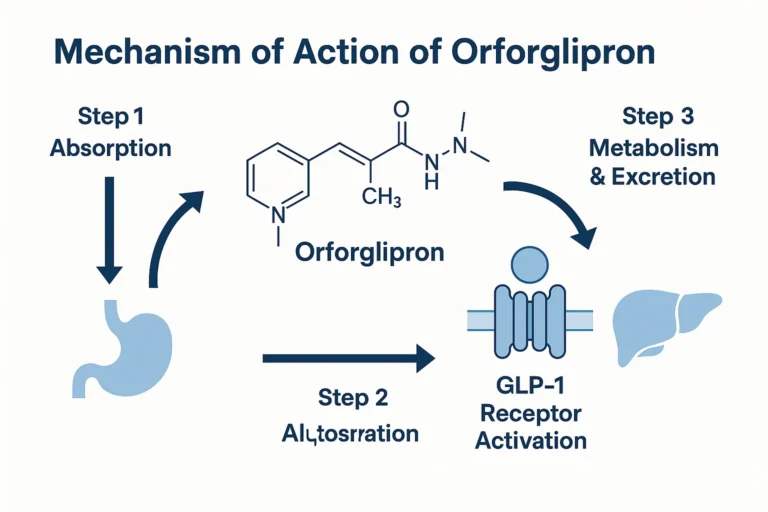
① Gastrointestinal Absorption and Distribution
– Rapid Absorption: Peak plasma concentration (Cmax) is reached 1-2 hours after dosing
– Distribution Characteristics: Plasma protein binding is ~99%, primarily distributed in tissues rich in GLP-1 receptors
– Unique Advantage: Unaffected by food (can be taken with meals)
② Targeted Activation of the GLP-1 Receptor
Orforglipron works through an allosteric activation mechanism:
③ Metabolism and Excretion
– Metabolic Pathway: Primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 (note interactions with azole antifungals and macrolides)
– Half-life: ~30-40 hours (suitable for once-daily dosing)
– Excretion: Primarily via feces (>80%)
Based on Phase III clinical trials (latest publication in 2024 NEJM):
– Glycated hemoglobin reduction: -1.8% to -2.3% (vs. -0.4% for placebo)
– Weight loss:
– Average weight loss over 36 weeks: -10.1 kg (15 mg dose group)
– Significantly superior to subcutaneous semaglutide (-6.2 kg)
– Gastrointestinal adverse reactions: Nausea (14% vs. 22% for semaglutide), vomiting (6% vs. 11%)
> Advantages Related to Mechanism of Action:
> Due to its partial agonist properties, orforglipron maintains efficacy while exhibiting a minimal effect of delayed gastric emptying—this explains why its incidence of nausea and vomiting is significantly lower than that of peptide GLP-1 agonists.
As an API expert, I must emphasize that the difficulty in synthesizing orforglipron lies in chirality control and impurity management:
Core Intermediate Synthesis Challenges
– We utilize asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation technology with a custom Ir(III) catalyst.
Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)
– Related Substances: Individual impurities <0.10%, total impurities <0.50%
– Genotoxic impurities: Nitrosamines <1 ppm (compliant with ICH M7)
– Crystalline Form Control: Stable Form II (hygroscopicity <0.2%) is required.
Orforglipron represents a triumph in small molecule drug design—it demonstrates that clever chemical structure design can break through the dominance of biologics. For our API companies, this means upgrading:
– Asymmetric synthesis capabilities
– Highly Potent API (HPAPI) production lines
– Continuous flow manufacturing processes
We firmly believe that the best drugs begin with the most precise synthesis. If you have any questions about Orforglipron products, please feel free to contact us. Tianming Pharmaceutical Group is dedicated to serving you!
Contact Email:sunqian0123@gmail.com

End-to-end supply chain for anti-diabetic intermediates. Covering DPP-4, SGLT-2 inhibitors & GPR40 agonists. Stable, compliant, scalable.
Drawing from on-the-ground experience in China’s top pharma clusters, this guide cuts through the jargon to reveal when to partner for complex innovation and when to buy from the workhorses of mature production.

This case study, based on publicly available academic literature and patents, focuses on the application of synthetic route optimization in improving the yield and purity of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs).

Leading provider of high-quality APIs and intermediates. Contact us for innovative solutions and expert support.